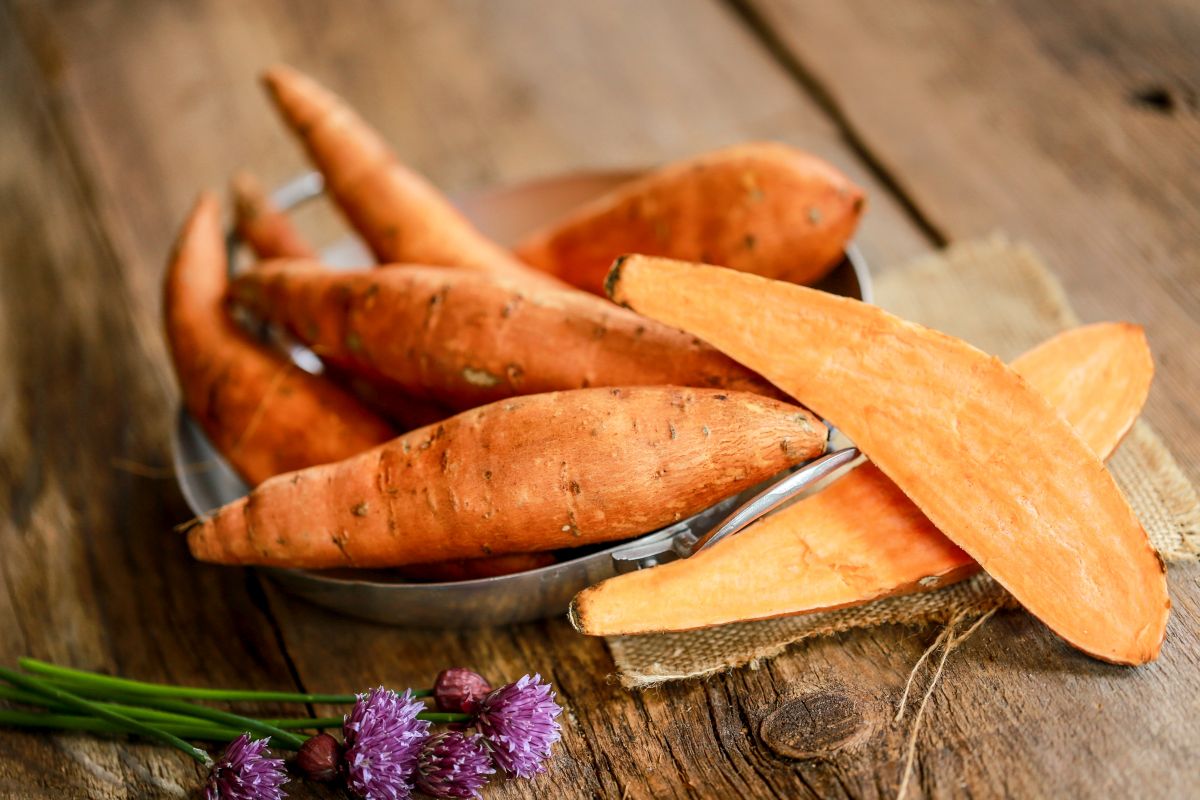
A vegetable that tastes sweet, is bright orange and still manages to be healthy – how cool is that? It’s enough to make even people who don’t like vegetables lick their lips. Read on to learn how you can use sweet potato to conjure up tasty, healthy snacks as quick as a flash, and discover the difference between this exotic tuber and our domestic potato.
What’s the difference between sweet potatoes and potatoes?
Did you know that sweet potatoes aren’t related to our potatoes at all? They aren’t part of the nightshade family (Solanaceae) – they’re belong to the morning glory family (Convolvulaceae) and have similar flowers to the field bindweed. Sweet potatoes taste more like pumpkin than potatoes. Unlike normal potatoes, you can eat the sweet tubers raw. Even its leaves are edible – but they’re a rare find in Germany.
A super tuber with valuable nutrients
Compared to these sweet super tubers, our potatoes look a bit pale – and not just when it comes to color. Sweet potatoes provide more of almost everything: more carbohydrates, more sugar (of course), and more fiber. That’s why they taste sweet but still fill you up. With just a little more fat but a great deal of fat-soluble vitamin E, 100g of sweet potato will provide a third of our daily vitamin E requirement. And they provide twice as much vitamin C as potatoes. As their lush orange color suggests, sweet potatoes are packed with carotenoids – valuable plant pigments that can protect our cells. However, their cornucopia of valuable nutrients mean that sweet potatoes also contain a third more calories..
| Nutritional values per 100g | Sweet potato | Potato |
| Energy/calories | 114 kcal | 77 kcal |
| Carbohydrate (total)Sugar
Fiber |
24 g5 g
3 g |
16 g1 g
1 g |
| Fat | 1 g | 0 g |
| Protein | 2 g | 2 g |
| Carotenoids | 7.900 µg | 5 µg |
| Vitamin E | 4,5 mg | 0,1 mg |
| Vitamin C | 30 mg | 15 mg |
More sugar, but smaller increase in blood sugar levels
Who would have thought? Although sweet potatoes contain more sugar, they don’t increase the blood sugar level as quickly as normal potatoes do. Some sweet potatoes even have a glycemic index* of under 55 when boiled, therefore within the recommended range. However, this depends upon the type of sweet potato as well as the method of preparation.
*The glycemic index (GI) indicates how quickly foods raise the blood sugar level.
Sweet potato – great for a quick snack
They look good, taste delicious and they’re healthy – but did you know that they are also quick and easy to prepare? Unlike our domestically grown potatoes, you can easily cook sweet potatoes in the microwave. Wash the tuber, pierce the skin in several places with a fork, wrap in a wet paper towel and cook in the microwave for around 15 minutes at full heat. Then slice open lengthwise, top with butter, salt and pepper or a tangy dip – and you’ve got yourself a light meal!
Sweet potato toast is just as quick. Slice a sweet potato evenly half a centimeter thick, set the dial on your toaster to four (around two-thirds of the full power) and toast the slices twice. Enjoy as a snack in between meals, for example with butter, cheese or tangy cream cheese.
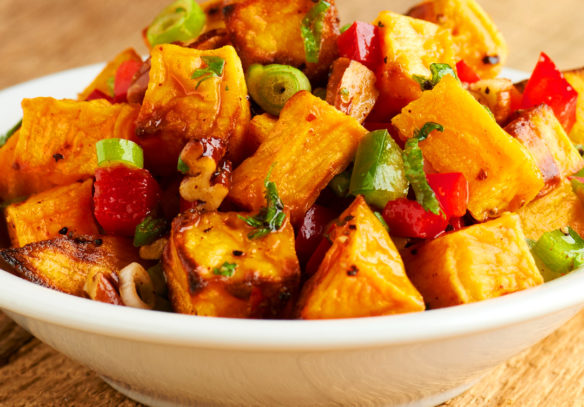

Sweet potatoes also taste wonderful as fries, mash, dumplings and soup. You can grate raw sweet potato into a salad. And its sweet flavor is perfect for desserts, baked goods and cakes. Are you convinced by the greatness of sweet potatoes? Then try our quick vegetarian sweet potato ragout with fresh cilantro.
Note: Since everyone’s health history and nutritional needs are so different, please make sure that you talk with your doctor and a registered dietitian to get advice about the diet and exercise plan that‘s right for you.